Research Excellence FrameworkImpact case studies
Explore impact case studies by Unit of Assessment
Allied Health Professions, Dentistry, Nursing & Pharmacy
Transforming the development & manufacture of medicine through continuous processing & advanced manufacturing technology research
Strathclyde research has been crucial in creating new methods and technologies for industrial pharmaceutical process development associated with continuous manufacturing and crystallisation (CMAC) generating impacts across the UK and international technology and pharmaceutical sectors. This has led to new product lines being developed (Alconbury Weston Ltd), and documented savings in development studies (Lilly) that have gone on to inform commercial manufacturing (AstraZeneca). Since August 2013, approximately GBP45,000,000 of savings and improvements have been realised by the 22 multinational and Small and Mediumsized Enterprises (SMEs) who have invested directly in proprietary analytical and process improvement projects.
Changes to cervical screening policies following the roll out of humanpapillomavirus (HPV) vaccination
Extensive national studies, including advanced analysis and modelling from Kavanagh, were the first population-based demonstrations of a reduction of cervical and precancerous disease due to the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, freely available in Scotland since 2008. The studies led the Scottish Government to change the age range of the Scottish Cervical Screening Programme and replace cytology with HPV testing as the initial stage of screening. Wider impact of the research caused UK policy makers to extend HPV vaccination to males, and the World Health Organisation (WHO) to advocate continued worldwide vaccination of girls aged 9-14. Global media coverage of the research also raised public awareness of successful vaccination initiatives at a time of growing misinformation related to vaccination.
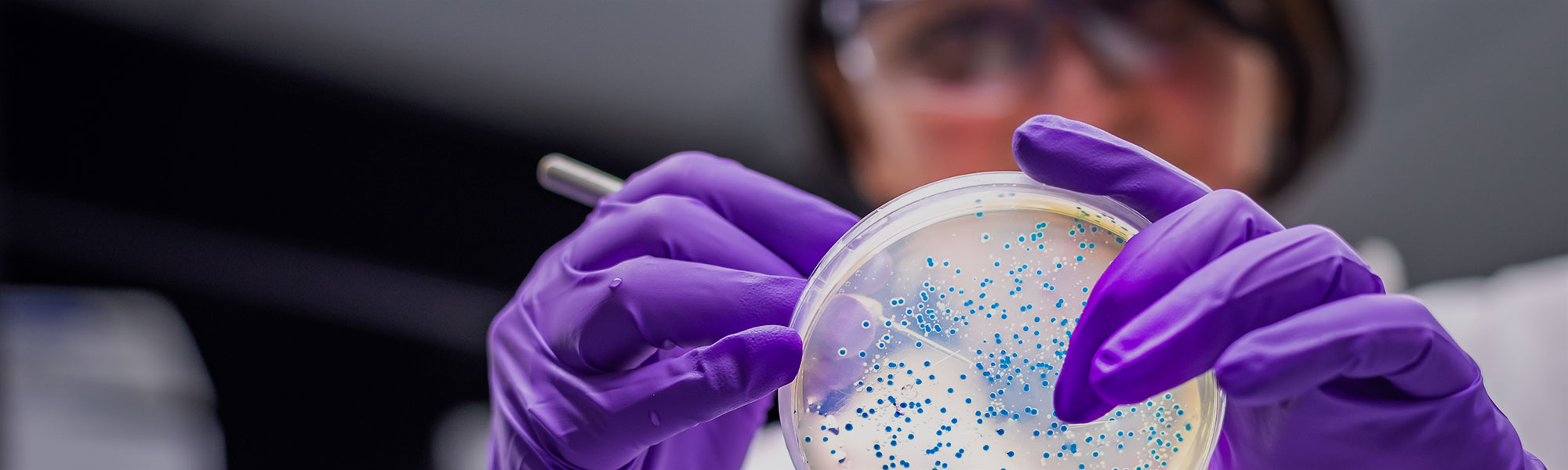
Rapid mass screening and detection of bacteria and toxins in food using improved automated immunoassays
Advances in immunology by Professor Stimson adopted by Solus Scientific Solutions Ltd. have expanded their food testing products, grown sales, increased employment and extended the company’s reach in microbiological testing. Rapid assays (<24 hours) for all strains of Listeria, Salmonella and Escherichia coli have been devised, augmenting Solus’ automated pathogen detection systems for these bacteria. Dedicated culture media based on the Strathclyde research allows sensitive detection of targeted organisms and control of false positive results. New kits for testing meat authenticity and allergen screen have also been introduced. Sales are up 43% from 2014 to GBP5,400,000 in 2019, with sales in 30 countries; and the number of employees increased from 24 to 43. Customers achieve higher productivity and efficiency owing to the greater sensitivity, simpler methodology and lower costs afforded through inclusion of Stimson’s discoveries in Solus products. In 2019, Perkin Elmer purchased Solus for USD34,000,000, increasing access to global food diagnostics markets.
Improved patient care through new antibiotic guidelines and resources
Thomson and Bennie’s research led to the development of and revisions to dosing guidelines for a range of antibiotics to treat severe infections. These guidelines are available online and used throughout NHS Scotland, NHS England and internationally. Additional resources produced by the researchers have resulted in a substantial improvement in effective antibiotic use in NHS Scotland and research findings were incorporated into commercial software packages to optimise antibiotic therapy for individual patients in USA, New Zealand and Europe. Through these developments, the research has supported optimal dosing of vancomycin, amikacin and gentamicin, which is vital for patient recovery from severe infection and an important aspect of tackling antimicrobial resistance.
Global & national guidelines for prevention of obesity through early-life physical activity
Since 2014, Strathclyde’s research and expertise around physical activity in early life has directly informed the development of new guidelines and implementation plans globally (WHO) and nationally (Canada, Australia, South Africa, USA, UK). By providing clear and accessible guidance to enable health professionals and primary caregivers to reduce screen time and increase physical activity in the under 5s, the research has strengthened campaigns to lower child obesity rates in order to improve cognitive development and academic attainment as well as prevent associated diseases in later life. Ensuring a new emphasis on the cognitive and educational benefits of obesity prevention and physical activity promotion for young children, this work has shifted public health messaging globally and laid the foundations for transformative behavioural change.
A new class of anti-infective drugs from DNA Minor Groove Binders
An outstanding, novel anti-infective drug discovered at Strathclyde is reaching the final stages of clinical trials. In the class known as DNA minor groove binders (S-MGBs), it completed Phase-IIa clinical trials in 2020, achieving total cures for the treatment of Clostridioides difficile infections, out-performing the existing benchmark (vancomycin), and is now approved for a Phase-III trial. Its novel multi-target mode of action explains why, to date, antibiotic resistance is not seen. MGB Biopharma, a new biotechnology company formed to develop the drug and sponsor the clinical trials, has raised over GBP11,000,000 in equity and public funding. MGB Biopharma expects the drug to be fully licensed and commercialised in 2024/5.
Safer use of high-risk medicines through data-driven quality improvement initiatives
Research led by Bennie on high-risk medicines (HRM) has shaped healthcare systems, providing clinicians with information to improve patient care. The team’s evaluation of the Scottish Patient Safety Programme – Pharmacy in Primary Care (SPSP-PPC) guided national policy including a Scottish Government commitment to support the safer use of medicines. This led to service redesign initiatives, which were implemented by all Scottish pharmacies to embed safe working practices and reduce risk concerning HRM. The initiatives have also been adopted by 55 New Zealand pharmacies. The Strathclyde research also informed a service review by the Scottish Government, which included new HRM measures in its 2018 National Therapeutic Indicator report, influencing Prescribing Action Plans within all 944 General Practices in Scotland. As a result, 30% fewer patients ≥65 years were exposed to HRM combinations since 2018.
Chemistry
A new class of anti-infective drugs from DNA Minor Groove Binders
An outstanding, novel anti-infective drug discovered at Strathclyde is reaching the final stages of clinical trials. In the class known as DNA minor groove binders (S-MGBs), it completed Phase-IIa clinical trials in 2020, achieving total cures for the treatment of Clostridioides difficile infections, out-performing the existing benchmark (vancomycin), and is now approved for a Phase-III trial. Its novel multi-target mode of action explains why, to date, antibiotic-resistance is not seen. MGB Biopharma, a new Scottish biotechnology company formed to develop the drug and sponsor the clinical trials, has raised over GBP11,000,000 in equity and public funding. MGB Biopharma expects the drug to be fully licensed and commercialised in 2024/5.
Creating enhanced capabilities in drug discovery research with GSK
A unique collaborative programme was devised to provide GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) employees in drug discovery with emerging scientific knowledge and access to alternative research methods based on the expertise of Strathclyde researchers. The initiative has had distinct impact on GSK’s scientific operations, the productivity and creativity of its researchers (26 patents; >95 GSK authored papers; >100 prizes), and the externally recognised reputation of the company (through multiple industry awards). GSK has further invested substantially in expanding the programme to include non-GSK personnel, which has now also benefitted other companies in the wider Healthcare sector. Since August 2013, 115 employee and non-employee participants have been engaged in the overall programme.
Accelerating drug development through novel iridium catalysts for enhanced hydrogen isotope exchange labelling
Iridium catalysts developed by Kerr have been adopted by the global pharmaceutical industry to achieve faster and more efficacious incorporation of radioactive and non-radioactive isotopes of hydrogen into a wider range of drug candidates. The catalysts enable key pharmacological tests to be carried out earlier and more effectively. These efficiencies have resulted in considerable time and money savings, a reduction in the amount of radioactive waste produced, and increased process safety. Wide and rapid adoption across the pharmaceutical industry has been facilitated further by Strem Chemicals, Inc., which has added three new Kerr catalysts to the existing range, and expanded sales through the relevant review period.
Physics
Photonics industry innovation & economic impact through the creation of the UK’s first Fraunhofer Centre
Strathclyde underpinning photonics research enabled the 2012 foundation and operation of the UK’s first Fraunhofer Centre, the Centre for Applied Photonics (Fh-CAP). This ground-breaking intervention in the UK innovation landscape represents a significant shift in Scottish government innovation policy. Working with Fh-CAP enables companies to accelerate technology development, develop new products, create and protect jobs and operate in international markets. Fh-CAP has exceeded its government-set targets, growing its 2020 turnover to GBP3,100,000 from contracted R&D. Since 2013, it has worked on 151 projects involving 116 companies, including 60 direct R&D contracts. Independent economic impact assessment has shown that these collaborations have resulted in additional turnover of GBP55,000,000 for Fh-CAP’s customers. Fh-CAP has a current staff of 34 and has provided training for 39 doctoral students many of whom now work in the vibrant UK photonics sector.
Economic & environmental impacts from laser spectroscopy spinout
Cascade Technologies Ltd is a spinout from the Department of Physics at the University of Strathclyde. Using a new approach to mid-IR spectroscopic gas sensing patented by Strathclyde, Cascade Technologies manufactures a range of gas sensors for both environmental and process monitoring that are sold either globally through Emerson or as original equipment manufacturer (OEM) systems to other manufacturers. These sensors are used in a range of gas sensing markets, including the shipping, car manufacturing, aerosol and food packing industries, where they have contributed to improved environmental pollution monitoring and food quality assurance. From 2014 to 2020 Cascade Technologies increased annual turnover from GBP5,800,000 to GBP10,300,000, and now employs 85 highly skilled staff, an increase of 42 from 2014.
Market-leading fluorescence products for global multidisciplinary markets
Strathclyde fluorescence lifetime research continues to contribute to growth in the commercial success of spin-out scientific equipment manufacturer HORIBA Jobin Yvon IBH Ltd (HORIBAIBH). The company develops products exploiting the technical, operational and cost advantages of high repetition rate semiconductor light sources and photon detectors for markets spanning life sciences, healthcare, chemistry, nanotechnology, and solar energy. Recent expansion of its facilities in Glasgow has supported growth in HORIBA’s leading 16% share of the USD152,000,000 global fluorescence spectroscopy market in 2013 to 22% in 2020. Recently the company introduced rapid fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) for the study in real time of live cells and transient species which is impacting on a range of medical applications. Strathclyde and HORIBA’s collaboration was recognised through Institute of Physics Awards in 2019 and 2020.
Diamond in photonics: economic impacts from new products, strategic industrial R&D investment & inter-company innovation
University of Strathclyde research has contributed to synthetic diamond manufacturer Element Six delivering economic impact on three fronts. First, it has underpinned new products, in turn opening up new markets. Second, as a significant component of a wider UK research effort in diamond, it contributed to Element Six’s decision to invest in its new UK-based Global Innovation Centre (GIC), which, since its establishment in July 2013, has created or secured jobs for scientists and technologists. Third, GIC facilities, in combination with Strathclyde underpinning research, have allowed Element Six to partner with companies to pioneer new products for markets including tools for computer chip manufacture and quantum technologies.
Mathematical Sciences
Developments in digital marketing through computational analysis of dynamic social media networks
Research at the University of Strathclyde into the analysis of large, evolving communication networks enabled the automatic identification of strong influencers and listeners within networks. This research led to the launch of Whisper, a commercially available, real time social planning software product, for the digital marketing company Bloom. Since August 2013, Whisper-related sales continued to grow for Bloom through high profile customers including Sky, Virgin Atlantic and ITV. In 2016, Bloom was acquired by Jaywing PLC, a UK-based digital marketing and advertising company, for GBP8,700,000. Whisper is a leading edge technology product for Jaywing and has been used to help major companies revolutionise the way they analyse and connect with target markets through social media platforms.
Informed management strategies & vaccination programmes for influenza, Human Papilloma Virus and COVID-19
As a long-standing recognised expert in statistical epidemiology, Robertson’s advice and evidence has informed government policy across many domains including planning for influenza pandemics, surveillance and vaccination programmes for seasonal flu, Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) immunisation (saving GBP500,000 annually) and management of the COVID-19 pandemic. He has a significant role on many health-related national and international committees, including the Scottish Government COVID-19 Advisory Group and the Scientific Pandemic Influenza Group on Modelling (SPI-M) which feeds directly into the UK Scientific Advisory Group for Emergencies (SAGE). Additionally, through Robertson’s joint appointment as Head of Statistical Research with Health Protection Scotland (HPS), Strathclyde has directly informed strategy for managing infectious diseases in Scotland.
Using stock assessment models to ensure sustainable use of international fishery resources
Mathematical analysis and modelling by Dr Cook at the University of Strathclyde has identified ways to improve the internationally accepted assessment of a shared cod stock to the west of Scotland. This work resulted in a review of the assessment and a consequent change to the estimated exploitation rate of the stock by the International Council for the Exploration of the Sea (ICES). On the basis of this and the related underpinning research, Cook has established international reputation that has led to him making significant contributions in similar activities, including: reviewing fisheries assessments conducted by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in the USA; being invited to assess the Marine Stewardship Council quality certification standard for fisheries worldwide; and influencing the UK Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) fisheries policy. Together, these activities are helping fishery managers around the world manage fish stocks more effectively, sustainably and profitably.
Computer Science & Informatics
Application of autonomous intelligent (AI) planning in drilling services industry automation
Underpinned by fundamental research in autonomous intelligent (AI) planning at Strathclyde, planbased control has been deployed by multinational energy industry technology company Schlumberger to support automation of the well construction process. This represents a stepchange in the technology applied to automatic drilling operations, with economic, efficiency, safety and environmental benefits, and has supported Schlumberger’s strategic objective to move its services up through levels of automation. A range of impacts have been realised including: technology innovation and new product development; improvements in well construction processes including time savings (for example a 20% increase in drilling rate) and cost savings (estimated at USD300,000 per well), improved drilling consistency and reduced environmental footprint; and economic impacts including product sales and industry partnerships (for example with Exxon Mobile and Honghua Electric). Schlumberger is now also applying this automation technology to borehole logging and logistics.
Economic impacts & improvements to professional programming practice arising from the addition of dependent types to the Glasgow Haskell Compiler
As a result of original research by Dr Conor McBride at the University of Strathclyde, dependent types are now embedded in the Glasgow Haskell Compiler, the de facto standard compiler for Haskell, a widely deployed programming language used in industry. As of 2020, 17% of open source Haskell libraries use features directly underpinned by McBride’s research. Dependent types in Haskell have been used to support millions of pounds worth of software development at Google, Habito, Galois, Digital Asset and Well-Typed, where it has been credited with improving programme robustness, speeding up development and deployment, and reducing costs.
Understanding & removing barriers to the wider adoption & implementation of digital health & care technologies
Research into the social, technological, and organisational barriers and facilitators to the adoption of digital health has led to practical applications in health and care practice throughout Scotland. Recommendations stemming from this research were adopted by the Scottish Government to directly inform Scotland’s Digital Health and Care Strategy. As a result of the evaluation methodology developed by the Strathclyde researchers, NHS Scotland now have quicker and easier ways to evidence and procure novel technologies, businesses have faster routes into the care market, and patients have a greater choice of technology for improving their quality of care. This research has directly supported the roll-out of two new diagnostic and screening technologies, and has furthered the expansion of the digital health industry.
Engineering
IMO regulations promote safety and innovation in the global maritime industry
Global maritime safety has been influenced by a range of collaborative research projects led by researchers in Naval Architecture Ocean and Marine Engineering at Strathclyde. Key findings were applied directly in the regulation-making process in the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) from January 2014 onwards; these regulations affect all commercial shipping operating up to December 2019, with important amendments informed by Strathclyde research introduced from January 2020. IMO regulations ensure a safety level is maintained, using a ‘risk-based’ approach to foster innovation in design and operation of over 12,000 commercial vessels since August 2013. IMO regulations have directly led to reduction in loss of and damage to ships, reduction in injuries and loss of lives at sea, and supported economic benefits to the global maritime and insurance sectors.
Transforming the development and manufacture of medicine through continuous processing and advanced manufacturing technology research
Strathclyde research has been crucial in creating new methods and technologies for industrial pharmaceutical process development associated with continuous manufacturing and crystallisation (CMAC) generating impacts across the UK and international technology and pharmaceutical sectors. This has led to new product lines being developed (Alconbury Weston Ltd), and documented savings in development studies (Lilly) that have gone on to inform commercial manufacturing (AstraZeneca). Since August 2013, approximately GBP45,000,000 of savings and improvements have been realised by the 22 multinational and Small and Mediumsized Enterprises (SMEs) who have invested directly in proprietary analytical and process improvement projects.
Growth of the Scottish small-satellite sector with global impact
Research undertaken at University of Strathclyde since 2004 was applied in the development of the UK’s first commercial CubeSat by Clyde Space Ltd., Glasgow, launched into space in July 2014. Over the next 5 years Clyde Space became a market leader, supporting around 30-40% of all CubeSat missions, and with a EUR7,600,000 annual turnover by the end of FY2019. The success of Clyde Space, together with availability of expertise from Strathclyde researchers, attracted other high value satellite and data analytics companies to the central belt of Scotland. Strathclyde research has led to capacity building and development of satellite technology in Mexico, South Africa, Namibia and Kenya, has influenced international strategy and planning, and has informed NASA’s approach to small spacecraft.
Reduced cost of generation & greater flexibility of low carbon electricity supply from UK wind farms
Multidisciplinary research led to the development of modelling tools for use in planning, installation and construction of offshore wind farms. Used in major UK offshore wind farm projects from 2014 by Scottish and Southern Energy, Iberdrola and its subsidiary Scottish Power Renewables, the modelling tools reduced a wide range of costs. Research also led to a change in strategy by National Grid ESO to enable renewable energy suppliers to provide reactive power to the grid, opening a new revenue stream for all windfarms from 2019. Electricity generation from offshore wind has become more economic, leading to further investment by SSE and SPR, and a boost to local economies. Offshore wind generation is increasingly adding to the energy mix available to consumers, assisting the renewables industry to meet UK Government low carbon targets.
Improving operational availability & revenue through enhanced management & life extension of nuclear power stations
Analytic software applications developed at the University of Strathclyde for the nuclear industry provide robust data interpretation and decision support regarding the health, condition and remaining lifetime of nuclear reactor cores, related plant and equipment. These support systems have been implemented and used by EDF (UK) and Bruce Power (Canada), and are critical tools in securing the supply of low carbon energy for the UK and Canadian economy and consumers. As a result of these advances, the nuclear industry has benefited from:
- enhanced safety cases for the Office for Nuclear Regulation in the UK, leading to the extension to planned operational lifetime of nuclear power stations
- accelerated plant availability and return to service following planned outages at nuclear power stations, providing significant time and cost savings
- improved management of nuclear facilities through the application of AI and data science
- new revenue streams for the nuclear supply chain
Innovative lighting system in healthcare settings reduces infection & benefits patients
Research at Strathclyde led to the development and commercialisation of a pioneering lighting system that can kill bacteria, fungi, and, under certain circumstances, viruses on surfaces and in the air. ‘Whole-room’ environmental decontamination is achieved with high-intensity narrowspectrum violet-blue light, which is safe for patients and staff, material and equipment, and can be continuously operated without the need for trained staff, or time consuming and potentially hazardous manual cleaning protocols. Licensees of the technology include two major US manufacturers, with implementation in over 300 healthcare facilities to date, with benefits to patient health, cost savings for hospitals, and economic benefits to commercial suppliers.
Economic & environmental benefits from widespread adoption of active power network management scheme
Research into active power flow management undertaken at the University of Strathclyde resulted in the successful delivery of an active network management scheme on the Orkney Islands in 2009 and a spin-out, Smarter Grid Solutions Ltd. Since August 2013, Smarter Grids Solutions has received GBP40,200,000 in revenue and grown their connected generators list to approximately 450MW. The technology has been utilised by leading power network companies to connect renewable energy generators in the UK, US and Europe, with ongoing projects globally, resulting in cheaper and greener energy available to customers, more efficient and flexible network operation, and cost savings for power generation companies and utility customers. All 6 UK distribution system operators have implemented active network management, with consistent expansion and investment in the technology since August 2013.
Improved standards & codes regulating GB & EU power networks ensure safe, stable & economic supply of electricity
A team of researchers, led by Bell and Dyśko, have made critical contributions to reliability, stability and cost of the electricity supply in Great Britain and Europe, through expert advice and changes to industry-wide technical codes and engineering standards. This has enabled renewable energy to increasingly form part of the energy mix available to consumers, while ensuring safety and security of supply. Research has informed capital expenditure and long term investment in the GB transmission system. Technical innovations and changes to standards have lowered cost barriers to renewable generation and demonstrated that renewables can provide a flexible source of energy, replacing thermal generation to achieve low carbon targets.
Research on metal-on-metal hip resurfacing implants leads to global withdrawal of implants, with economic and health benefits for patients worldwide
Research by Professor Grant directly contributed to the Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency’s (MHRA) medical device alert and subsequent product recall in 2010 for many DePuy metal-on-metal hip replacement and resurfacing implants. Since August 2013, the company has faced lawsuits in USA, Canada, UK, Ireland, Australia and India, with over GBP4,500,000,000 of compensation awarded so far. Withdrawal of other manufacturer’s metalon-metal implants followed from 2015 onwards, with these companies also facing substantial claims for compensation. Updated MHRA guidelines in 2017, with input from Grant, highlighted the need to monitor Cobalt and Chromium in blood of patients who had undergone hip replacement. The medical profession and the wider public have become increasingly aware of the risks of raised levels of cobalt and chromium, and designs have improved as a result.
Innovative technologies for field ophthalmology improve access to healthcare in low- and middle-income countries and in the UK
Researchers at the University of Strathclyde developed a low-cost smartphone add-on to be used by community operators for the imaging of the back of the eye. The device was trialled in African countries (2013-14) and made available commercially through a spin-out company from 2016. The innovation has been described as exemplary in World Health Organization guidelines. Research led to further innovations in technology for telemedicine, rolled out in several Scottish NHS boards, where it has reduced the need for travel to and wait for appointments, reduced costs, improved the service to patients, with earlier identification of urgent cases. Stimulated by the COVID-19 response, the technology has been introduced into national policy and in platforms with global distribution.
Architecture, Built Environment & Planning
Built environment modelling & monitoring to support the clean energy transition
Research conducted in the Energy Systems Research Unit (ESRU) at Strathclyde evolved the state-of-the-art in software tools for the planning, design and monitoring of low carbon urban environments. These tools are made available under an open source licence and have been applied by ESRU staff and construction industry practitioners worldwide to adapt to the changing energy landscape, inform performance improvements and energy demand reduction in urban contexts, and expand construction business offerings. The models have also informed energyrelated policy and standards intended to drive societal change, including at the city scale, and the identification of new business opportunities for technology deployments.
Protecting occupant health, reducing energy & lowering carbon emissions through building ventilation regulation & control
Research into energy reduction and ventilation undertaken by the University of Strathclyde has improved building performance in Scotland and the UK to protect occupant health, save energy and reduce carbon emissions. Specifically, since August 2013 it has:
- protected occupant health by influencing Scottish common law
- shaped UK Government policy and public health advice to reduce COVID-19 transmission
- informed Building Regulations and industry guidance to improve building performance in Scotland and the UK
Business & Management Studies
Driving workplace innovation to transform work and workplaces in Scotland
Workplace Innovation (WI) research at Strathclyde’s Scottish Centre for Employment Research (SCER) drove new policy development and practical change within businesses through the creation of a Scotland-wide multi-stakeholder collaborative network. This network co-created interventions that underpinned adoption of WI as a policy priority by the Scottish Government and public agencies, resulting in the promotion and resourcing of WI to improve business performance and national economic performance. Public agencies funded and delivered business support for WI that improved business performance in more than 700 businesses. Moreover, businesses who participated directly in the research (over 50) and many who engaged with the research (over 500) adopted innovative workplace practices that improved performance and employee experience. The research also equipped unions to promote WI in bargaining to the benefit of members as well as driving innovation and modernisation within the bodies themselves.
Advancing fair work policy and practice in Scotland to benefit workers, businesses and society
Strathclyde’s research on job quality, skills utilisation and workplace partnership has shaped Scotland’s approach to fair work and driven its implementation and ongoing development. By informing the Working Together Review, the research approach and findings drove the establishment of an independent Fair Work Convention, and underpinned the development of the FWC Fair Work Framework. Since 2016, this Framework has influenced Scottish Government policy (the most notable outcome being the publication and pursuit of a Fair Work Action Plan), shaped the priorities and practices of public agencies delivering business support, and changed the practices of employers and unions. This has contributed to improvements in job quality, particularly in relation to job security and effective voice, and ensured targeted responses to particular challenges, including sector-specific issues and the ramifications of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Improving policy-relevant analysis in the UK, Europe and USA through novel macroeconometric methods
Financial institutions and government bodies have used the macroeconometric methods created by Strathclyde researchers to enhance regional and national policymaking in the UK, Europe and the USA. The new methods produced more accurate and timelier estimates of macroeconomic variables, including regional economic activity and inflation. Applications of the methods have strengthened the economic analysis undertaken by the UK Office for National Statistics, Scottish Fiscal Commission, Bank of England, European Central Bank, European Commission and US Federal Reserve Banks. Decision-making within and beyond these bodies has been informed. Aspects of the research also augmented economic analysis and commentary disseminated to stakeholders and the public by global businesses (e.g. PricewaterhouseCoopers) and media outlets (e.g. Financial Times).
Improved patient outcomes through evidence-based decisions by Scottish and global health organisations
Modelling methods research at Strathclyde enabled the formulation and implementation of health care policy to improve patients’ outcomes in Scotland and internationally. At national level, this strengthened service delivery in Scotland’s National Health Service (NHS), through the scale-up of virtual clinics and sustained delivery of care in hospitals and care homes during the Covid-19 pandemic. Internationally, Strathclyde’s research increased analytical capacity at the World Health Organisation and Global Fund leading to informed strategic allocation of development aid in support of a wide portfolio of health initiatives to reduce morbidity and mortality.
Enhancing entrepreneurial policy, ecosystems and firm growth
Research undertaken by Strathclyde’s Hunter Centre for Entrepreneurship, Strategy and Innovation has informed entrepreneurial policy, improved Scotland’s entrepreneurial ecosystem and supported the growth of entrepreneurial ventures. Through collaboration with the Scottish Government, regional enterprise support organisations and membership organisations, this research has: informed the development of a policy framework to accelerate Scotland’s entrepreneurial ecosystem (Scotland CAN DO); contributed to raising the global profile of Scotland’s entrepreneurial ecosystem from 13th to 5th in the Global Entrepreneurship Development Index (GEDI) of innovation-driven nations; and informed the design of a suite of entrepreneurship leadership programmes focused on scaling high potential ventures, including the ScaleUp Institute-endorsed Growth Advantage Programme.
Enhancing analytical capacity and knowledge through economic modelling to strengthen regional policy-making in Scotland, Northern Ireland and Europe
Through the advancement and application of Computable General Equilibrium (CGE) modelling, Strathclyde’s Fraser of Allander Institute (FAI) has strengthened regional policy-making by enhancing analytical capacity and knowledge within Scotland (Scottish Government, City of Glasgow Council, Scottish Policy Foundation), Northern Ireland (Northern Ireland Executive) and Europe (European Commission). By enabling effective and efficient regional economic modelling and multi-sectoral analysis, this research has supported and strengthened evidence-based policy development in response to a range of pressing issues including climate change and Brexit.
Enhancing decision-making through new modelling methods of dependent risks to improve engineered systems and complex projects
Strathclyde research recognised that dependencies between events must be captured to properly assess risk; otherwise risk exposure will be understated and opportunities to learn from related events will be lost. Novel methods and tools, based on the research of the group, have been created for problem structuring, modelling, elicitation, inference and decision support. These have been used in technical risk management for new product development, informed modelling used for risk management of the GB rail system, reduced the costs of renewable energy project bids, influenced a large EU arbitration case, enabled city resilience planning and been referenced by international standards (ISO 31010, IEC 61164).
Tackling in-work poverty in the UK by demonstrating the business case for a real Living Wage
Responding to concerns that the lack of a business case for paying a real Living Wage was hindering adoption, Strathclyde research provided evidence that Living Wage accreditation enhances financial and social capital for employers as well as improving pay and conditions for low-paid workers who are most at risk of in-work poverty. This evidence underpinned the Living Wage Foundation (LWF) campaign from 2015, persuading over 6000 companies to become accredited real Living Wage employers between 2015 and 2019 to the benefit of more than 240,000 low-paid workers. Combined with in-depth analysis of implementation challenges within the Scottish social care sector, this research has increased and improved adoption of the Living Wage by strengthening LWF strategy and operations, and informing UK, Scottish and Welsh government policy. It has also shaped the development of a global Living Wage standard.
Equipping trade unions to improve employment relations through achieving performance management reform
Responding to trade union concerns, Professor Taylor’s research provided evidence of the nature and implications of poor performance management practice in the public and private sectors which equipped UK trade unions to campaign effectively for Human Resources Management (HRM) reform to improve employment relations. Achieved through dissemination of Taylor’s report for the Scottish Trade Union Congress and the application of its findings by the Communication Workers Union, Unite the Union’s Finance and Legal Sector, Accord and the Public Commercial Services Union, numerous public and private sector organisations reviewed and improved their approach to performance management to the benefit of both employees and employers. At least 238,000 employees have benefitted from these improvements.
Law
Improving Equality of Workers’ Access to Justice
Research into the employment tribunal and claimants’ access to justice benefited claimants and respondents, policy makers, civil society organisations, judiciary, lawyers and advice organisations in Scotland. Specifically, the equality of access and services provided to claimants, particularly litigants in person, improved. This included how employment judges approached case preparation and hearings; employment advisors’ delivery of advice and case preparation; the Law Society of Scotland’s abandonment of the proposal to withdraw legal aid for employment cases; UK and Scottish government policies on tribunal fees and the effectiveness of workers’ rights.
Improving stop & search practice by Police in Scotland
Dr Genevieve Lennon’s research on stop and search led to a change in police law and practice in Scotland, notably a new Code of Practice. The Code, effective from 2017, regulates police practice during the execution of a stop and search, and provides the public with information about their rights. Stop and search incidences went down, with Glasgow seeing a 59% reduction in 2017/18 compared with the previous year. In 2019, the Advisory Group on Stop and Search noted that: the new recording system was more reliable and accurate; police officers were applying stop and search more judiciously; and there was increased public confidence in the tactic.
Evaluating & Enhancing Quality in Legal Professionals through Peer Review
Based significantly on Paterson’s research, scheduled peer review programmes were established to evaluate the quality of legal aid work across the UK from 2002. These quality assurance programmes continue to date, with 55,053 cases from over 6,000 legal aid firms reviewed across the UK since August 2013, leading to enhanced quality of service for legal aid recipients who rely on the service to access necessary legal support and representation. With the success of the UK models and the rising value placed on quality assurance of legal aid services internationally, Paterson has been invited to present and advise on the introduction of peer review models extensively, directly contributing to its adoption in the Netherlands, New Zealand, Moldova, Ukraine, and China.
Politics & International Studies
Gerrymandering & partisan bias: informing the courts, non-governmental organisations & public debate in the United States
Conducted in collaboration with international partners, McGann’s ground-breaking research into gerrymandering in the US has significantly influenced litigation on electoral districting in the US courts since 2016. It has been cited on multiple occasions before the US Supreme Court by plaintiffs, expert witnesses and prominent politicians, most notably the late Senator John McCain and Senator Sheldon Whitehouse. It has been used by multiple plaintiffs as a foundation for gerrymandering complaints to state and district courts. McGann’s research and engagement has also influenced the strategy of US non-governmental organisations (NGOs), both in the issues they campaign on and the state-level legislation they have drafted. Finally, McGann’s research has informed the wider debate and public understanding of redistricting and voting rights issues through coverage in prominent media outlets.
Influencing cohesion policy & territorial cooperation in Europe, the UK & the Caribbean through comparative public policy analysis
Research by the European Policies Research Centre (EPRC) on EU Cohesion Policy has influenced policy decisions at international, national and sub-national scales. Research on the institutional dynamics of Cohesion Policy reform was used to facilitate intergovernmental dialogue among EU Member States and the formation of Germany’s governmental negotiating position in EU policy and budgetary reforms in 2018-20. Studies of governance also informed decisions by the Scottish Government on its post-Brexit replacement of Cohesion Policy. Research on the perception of Cohesion Policy among EU citizens was used by the European Commission to justify a new policy priority and legislative changes. Comparative research on EU policy experience also provided the basis for a new cohesion policy by the Caribbean Community (CARICOM).
Shaping energy, climate & industry policy to realise wider economy & societal benefits in transitioning to net zero
Through direct engagement with public policy stakeholders at Scottish, UK and international levels, Strathclyde’s Centre for Energy Policy (CEP) research on understanding, quantifying and building consensus around the wider economic impacts of different industry, household and policy actions has shaped policy development to support low carbon transition to mid-century net zero carbon targets. This includes use of CEP’s research by the UK Government Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS) to support a 2018 policy strategy on carbon capture, usage and storage for industrial decarbonisation, and to inform the UK Chancellor’s July 2020 decision to allocate public spending to support residential energy efficiency.
Social Work & Social Policy
Enhancing justice services to advance social integration and desistance
The pressure for better policies and practices to promote desistance from crime is a longstanding problem for criminal justice systems and the societies they serve. Strathclyde’s research around supporting desistance (giving up crime) and social integration has driven the introduction of a new desistance-informed, strengths-based assessment and short-term intervention framework across the Scottish Prison estate. It has also directed a shift in governance practices in community justice contexts leading to the diversification of and innovations in service delivery and provision, and shaped policies encouraging service-user involvement in community justice. Furthermore, it has incentivised the development of new work integration social enterprises in both Scotland and Canada; informed Scottish legislation on progressive approaches to the disclosure of criminal records; and encouraged policy-makers across the UK to recognise the need to develop work integration social enterprises in justice contexts to address labour market inequalities for people with convictions.
‘Here to Stay’ - Influencing policy, improving public services for Eastern European migrant young people & informing public debate and attitudes to migration
Research conducted at Strathclyde has demonstrated that young people born in Central and Eastern Europe who have settled in the UK are disadvantaged in terms of rights and opportunities, including their education outcomes, well-being and access to services. This research, which involved work with over 1,500 EU-born young people, informed a unique programme of training, policy and community activities. It has led to significant improvements in policy and practice supporting migrant groups. Events and training materials for practitioners enhanced their understanding of young people’s experiences and barriers to full participation in society, including experiences of discrimination and loss of rights post-Brexit. Research was used to tackle gaps in service provision and improve public understanding of EU migration across the UK and internationally through blogs, media contributions, campaigns and art exhibitions.
Education
Improving classroom practice & learning through philosophy with children
Cassidy’s research demonstrating the benefits of Philosophy with Children (PwC) and extensive engagement activities led teachers, schools, local authorities and NGOs to adopt the approach. Through this increased uptake, the research has supported children’s development across the curriculum, their personal development, their agency, and their cognitive and social skills. Importantly, this includes benefits for children with Additional Support Needs (ASN) or who are marginalised. Teachers have reported wide changes to their practice outside of PwC sessions, including greater inclusivity, more active engagement with their pupils, enhanced relationships and improved pedagogy. As a consequence of teacher training delivered by Cassidy, it is estimated that thousands of children will have benefited from this approach since August 2013.
Improving teaching & assessment practice and informing policy in literacy & attainment
Strathclyde literacy researchers developed the Strathclyde 3 Domains assessment tool and associated pedagogies that raised literacy attainment and increased teacher autonomy. Directly benefiting 18,700 pupils in Scotland, the tool enhanced teacher noticing, knowledge and attitudes, raised attainment, narrowed the attainment gap associated with poverty, and shortened the tail of underachievement. It has also informed national policies, pedagogies and assessments in Scotland, was labelled ‘outstanding’ by HMIE, and been embraced by Scottish government ministers and teacher educators in the EU, USA and Australia.
Closing the poverty attainment gap in education through changing policy & practice
Research for the Joseph Rowntree Foundation on closing the attainment gap underpinned the Scottish Government’s 2015 amendment to the Education (Scotland) Bill and subsequently the 2016 Act, which required Local Authorities to report on the extent of the poverty-related attainment gap and efforts to reduce it, a GBP750,000,000 Attainment Fund for schools, and a National Improvement Framework providing practitioner guidance. Evaluation of these policies have demonstrated a significant increase in pupil attainment and a reduction in the poverty-related attainment gap. Educators in Scotland, Ghana and Malawi have also adopted the recommendations from the research to improve pupil engagement and performance, reduce absenteeism and increase parental involvement.
English Literature & Language
Embedding Victorian working-class poetry, literature & song into education, heritage & the arts
Professor Kirstie Blair’s research uncovered a rich history of industrial workers’ engagements with literary culture and demonstrated the cultural importance of working-class poetry in Victorian Scotland. Blair’s wider activities have enabled the public to connect with these works, through the development of educational, heritage and cultural resources. Ultimately, this has raised awareness of little-known literary cultures, promoted pride in the local poetic productions of Scotland and Northern England, and inspired the creation of new cultural artefacts. Collaborators, such as the National Railway Museum and Stanley Mills, benefited from wider audiences and new resources, and changed their practice as a result.
Promoting a culture of responsible media reporting & consumption
Working under the research theme of Responsible Media, Eckler, Boyle and Duncan examine social media, body image and mental health; gender equality and representation; and media coverage of traumatic content, such as suicide. The research findings have been translated into accessible resources, such as toolkits for journalists, media guidelines, public talks, blogs, podcasts, MOOCs, and activity packs, which have been actively taken up and used by media companies, journalist associations, third sector organisations, individuals, and government. This has resulted in improved training and awareness of responsible reporting in media, increased public awareness of responsible media consumption, and has informed government policy related to social media and gender equality.
After partition: making Punjabi heritage inclusive across borders
Literary research on travel, migration, and refugees has enabled Mahn to work with two organisations to address disconnected and marginalised heritage in and around Amritsar, a city with a contested heritage narrative. By working with the Cultural Resource Conservation Initiative and the grassroots NGO, Preet Nagar Residency, Mahn created change in mainstream heritage management and worked with creative communities along the Indo-Pak border to generate new work on ‘missing’ stories about Punjab and its history. In particular, Mahn has integrated community perspectives into government heritage projects, changed attitudes to heritage and facilitated belonging, and created new educational, cultural, and economic opportunities for Punjabis through heritage work.
History
Using oral histories to create awareness of industrial heritage for social & economic benefit
Through extensive research, training, consultancy, community and work placement activities, McIvor’s work ensured that the collection and interpretation of oral history was significantly enhanced across the museum, heritage and local community sectors in Scotland, with marked social and economic benefits. This deepened understanding of Scotland’s industrial heritage and history of working lives, whilst marginalised voices were made more visible. A series of corporate oral histories enriched companies’ perception of their workers’ role in their development, and boosted their economic activities through adding heritage narratives to their marketing tools. McIvor’s research considerably augmented societal understanding of occupational disease and advocacy, created widely used open access cultural resources, whilst a new Massive Open Online Course (2019) deepened public and professional awareness of mining history and heritage.
Challenging perceptions & informing debate around controversial health issues
Through engagement with health and education professionals, advocates and the public, Professor Smith’s award-winning historical research has challenged perceptions and informed debate around three controversial health issues: food allergy, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and preventive approaches to mental health. Demonstrating the unique insights to be gained from rigorous historical analysis, the findings from Smith’s extensive archival and oral history research have: influenced health policy and practice in the USA, Canada and UK; informed preventive mental health approaches in Scottish schools; and deepened public understanding through media engagement and cultural influence.